Medicine - Veterinary > Civil Veterinary Departments > Indian Civil Veterinary Department memoirs > No. 2 - Collected notes
(234) Page 53
Download files
Individual page:
Thumbnail gallery: Grid view | List view

53
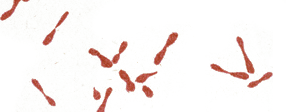
RATS.
Rat No. 104 was inoculated with a loopful of H. S. agar
culture and died on the 6th day.
Lesions were only very slight enteritis and a small swell-
ing at the seat of inoculation. No tracheitis was present.
By passage from rat to rat the bacillus increases in
virulence for the rat.
FOWLS.
Hen No. 60 was inoculated subcutaneously with 1 c.c.
emulsion of 24 hours old H. S. agar culture. There was no
result, not even a local reaction, but the control rabbit died
in 23 hours.
29 days later the fowl was reinoculated without result,
but the control rabbit died in 22½ hours.
Hen No. 61. was inoculated subcutaneously with ½ c.c.
bouillon culture of H. S. There was a slight local œdema
which passed off in 3 days. The control rabbit died in 22½
hours. A 2nd inoculation of this hen had similar results.
WHAT IS THE NATURAL METHOD OF INFECTION?
The disease is most common after rain, as in the
monsoon in July and August, and also after the Christmas
rains.
Almost any shower of rain during the winter months
will give rise to a few cases in the affected districts.
The districts, in which the disease is found, are low-
lying and damp ones, such as the land near the big rivers
and the land intersected by them.
The accepted theory is that the bacillus lives in the
damp soil or in the soil water and that the disease appears
during the rains when the soil water rises and that animals
become infected by ingestion.
Experiments prove the ingestion theory to be wrong
Several young buffaloes have been fed on enormous
doses of virulent culture (1,000 c.c.) in their gram and bran,
and at the same time were kept on the coarsest grass which
they could eat and which was calculated to cause wounds in
the mouth and stomach, but in no case did infection result.
Set display mode to: Large image | Zoom image | Transcription
Images and transcriptions on this page, including medium image downloads, may be used under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International Licence unless otherwise stated. ![]()
| India Papers > Medicine - Veterinary > Civil Veterinary Departments > Indian Civil Veterinary Department memoirs > Collected notes > (234) Page 53 |
|---|
| Permanent URL | https://digital.nls.uk/75512649 |
|---|
| Shelfmark | IP/RA.10. |
|---|---|
| Additional NLS resources: | |