Medicine - Institutions > Lock hospitals > Annual report on the lock hospitals of the Madras Presidency > Annual report on the military lock hospitals of the Madras Presidency, for the year 1883
(319) Page 6
Download files
Individual page:
Thumbnail gallery: Grid view | List view
6
ANNUAL REPORT ON THE
stations included in the above return was 324.09. Since that period the annual
rates, although variable and high, have still manifested some signs of a permanent
decline. Tables G and H, showing the prevalence of venereal diseases at stations
at which Lock Hospitals were in operation and at those at which they did not exist,
are given as usual in the Appendix.
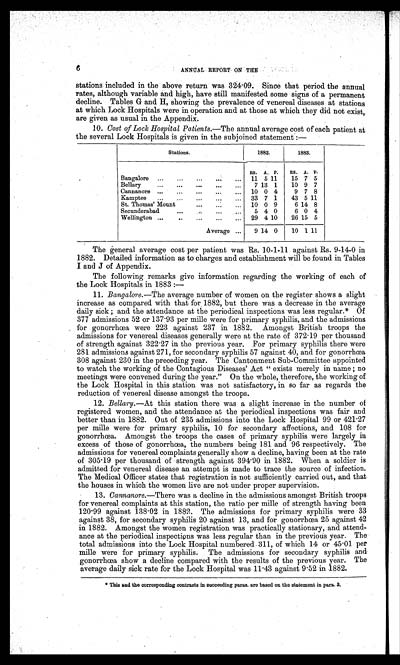
10. Cost of Lock Hospital Patients.—The annual average cost of each patient at
the several Lock Hospitals is given in the subjoined statement :—
| Stations. | 1882. | 1883. | ||||||||
| Rs. | A. | P. | RS. | A. | P. | |||||
| Bangalore | 11 | 5 | 11 | 15 | 7 | 5 | ||||
| Bellary | 7 | 13 | 1 | 10 | 9 | 7 | ||||
| Cannanore | 10 | 0 | 4 | 9 | 7 | 8 | ||||
| Kamptee | 33 | 7 | 1 | 43 | 5 | 11 | ||||
| St. Thomas' Mount | 10 | 0 | 9 | 6 | 14 | 8 | ||||
| Secunderabad | 5 | 4 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 4 | ||||
| Wellington | 29 | 4 | 10 | 26 | 15 | 5 | ||||
| Average | 9 | 14 | 0 | 10 | 1 | 11 | ||||
The general average cost per patient was Rs. 10-1-11 against Rs. 9-14-0 in
1882. Detailed information as to charges and establishment will be found in Tables
I and J of Appendix.
The following remarks give information regarding the working of each of
the Lock Hospitals in 1883 :—
11. Bangalore.—The average number of women on the register shows a slight
increase as compared with that for 1882, but there was a decrease in the average
daily sick ; and the attendance at the periodical inspections was less regular.* Of
377 admissions 52 or 137.93 per mille were for primary syphilis, and the admissions
for gonorrhœa were 223 against 237 in 1882. Amongst British troops the
admissions for venereal diseases generally were at the rate of 372.19 per thousand
of strength against 322.27 in the previous year. For primary syphilis there were
281 admissions against 271, for secondary syphilis 57 against 40, and for gonorrhœa
308 against 230 in the preceding year. The Cantonment Sub-Committee appointed
to watch the working of the Contagious Diseases' Act " exists merely in name ; no
meetings were convened during the year." On the whole, therefore, the working of
the Lock Hospital in this station was not satisfactory, in so far as regards the
reduction of venereal disease amongst the troops.
12. Bellary.—At this station there was a slight increase in the number of
registered women, and the attendance at the periodical inspections was fair and
better than in 1882. Out of 235 admissions into the Lock Hospital 99 or 421·27
per mille were for primary syphilis, 10 for secondary affections, and 108 for
gonorrhœa. Amongst the troops the cases of primary syphilis were largely in
excess of those of gonorrhœa, the numbers being 181 and 96 respectively. The
admissions for venereal complaints generally show a decline, having been at the rate
of 305.19 per thousand of strength against 394.90 in 1882. When a soldier is
admitted for venereal disease an attempt is made to trace the source of infection.
The Medical Officer states that registration is not sufficiently carried out, and that
the houses in which the women live are not under proper supervision.
13. Cannanore.—There was a decline in the admissions amongst British troops
for venereal complaints at this station, the ratio per mille of strength having been
120.99 against 138.02 in 1882. The admissions for primary syphilis were 33
against 38, for secondary syphilis 20 against 13, and for gonorrhœa 25 against 42
in 1882. Amongst the women registration was practically stationary, and attend-
ance at the periodical inspections was less regular than in the previous year. The
total admissions into the Lock Hospital numbered 311, of which 14 or 45.01 per
mille were for primary syphilis. The admissions for secondary syphilis and
gonorrhœa show a decline compared with the results of the previous year. The
average daily sick rate for the Lock Hospital was 11.43 against 9.52 in 1882.
* This and the corresponding contrasts in succeeding paras. are based on the statement in para. 3.
Set display mode to: Large image | Zoom image | Transcription
Images and transcriptions on this page, including medium image downloads, may be used under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International Licence unless otherwise stated. ![]()
| Permanent URL | https://digital.nls.uk/75113016 |
|---|